Centralized Vs. Decentralized Digital Currencies
This article explores the key differences between centralized and decentralized digital currencies. It explains how each system operates, their pros and cons, and why understanding their structure is essential for anyone navigating the world of crypto.
Go Back
🕒 7:50 AM
📅 May 03, 2025
✍️ By Raphbeo
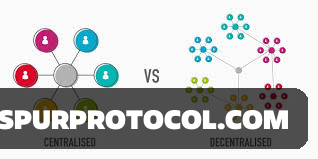
Not all digital currencies are built the same. The key difference lies in how they’re controlled—centralized vs. decentralized.
Centralized currencies are issued and managed by a single authority—usually a government or bank. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) fall into this category. The issuer has full control over supply, distribution, and monitoring. It’s similar to how fiat currencies work, just in a digital form. Think of Nigeria’s eNaira or China’s digital yuan.
Decentralized currencies, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, work without a central authority. Instead, they rely on a global network of computers (nodes) that maintain a public ledger using blockchain technology. No single person or group can control the network. This makes them resistant to censorship, inflation, or policy manipulation.
The main trade-off? Centralized systems are faster and easier to regulate but come with less privacy and more government control. Decentralized systems offer freedom and transparency, but can face scalability issues and are harder to regulate.
Understanding this difference helps you decide where to place your trust—whether you prefer convenience and control or autonomy and transparency. Both systems have roles to play in the future of finance.
