Consensus Mechanisms Evolution Proof-Of-Stake And Proof-of-Work Alternatives
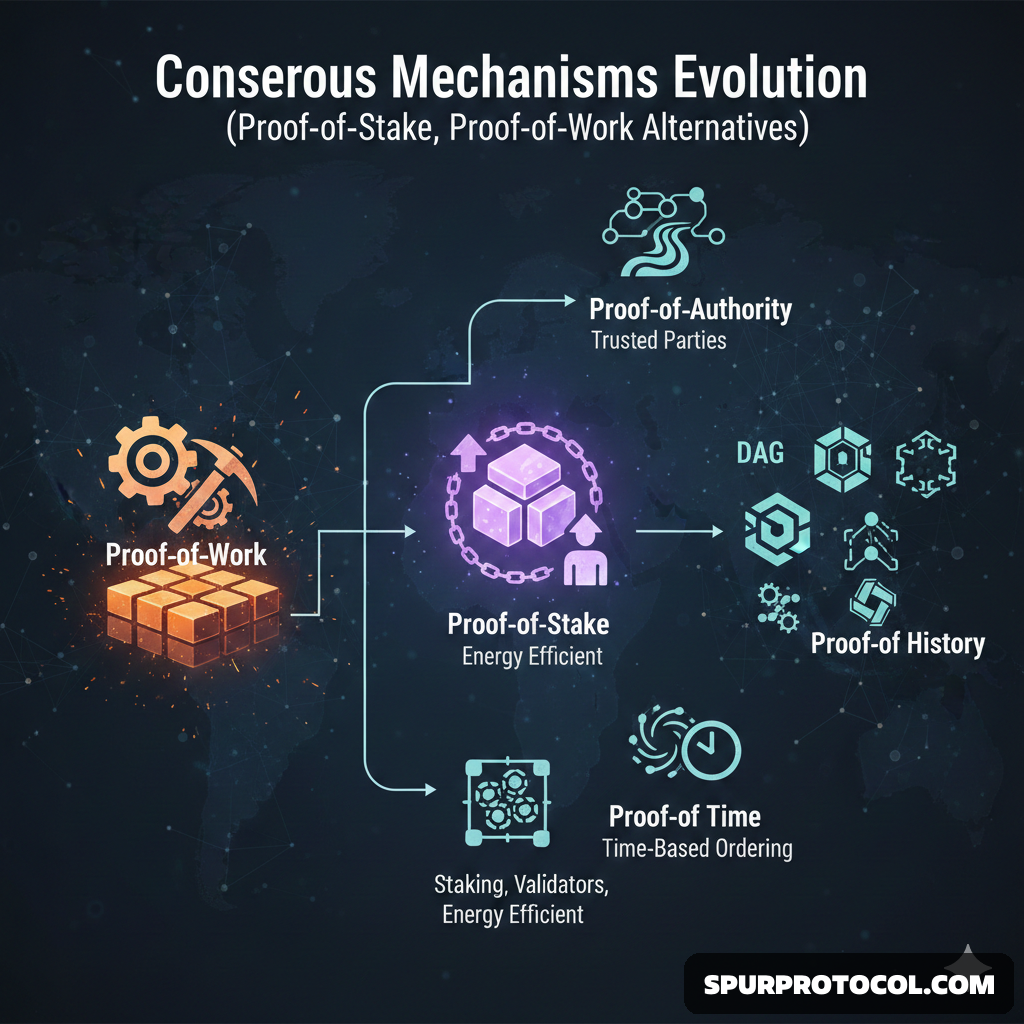
The evolution of blockchain consensus mechanisms has transitioned from resource-heavy computational competitions to energy-efficient, economic, and identity-based models to solve the "blockchain trilemma" of balancing security, decentralization, and scalability.
Go Back
🕒 8:03 PM
📅 Dec 19, 2025
✍️ By chyneyz
1. Foundation:
Proof-of-Work (PoW)
Introduced with Bitcoin in 2009, PoW requires "miners" to solve complex cryptographic puzzles to validate transactions.
Mechanism:
Competitive mining where the first to solve the puzzle earns the right to add a block.
Strengths:
High security and deep decentralization; proven resilience over a decade.
Weaknesses:
Massive energy consumption and limited transaction speed (scalability issues).
2. The Shift: Proof-of-Stake (PoS)
PoS emerged as a sustainable alternative, most notably with Ethereum's 2022 transition which reduced its energy use by 99.84%.
Mechanism:
Validators are selected based on the amount of cryptocurrency they "stake" as collateral.
Variations:
Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS):
Token holders vote for a fixed number of delegates to validate transactions, increasing speed at the cost of some decentralization (e.g., EOS, Tron).
Nominated Proof-of-Stake (NPoS):
Holders nominate trusted validators (e.g., Polkadot).
3. Modern Alternatives & Specialized Mechanisms
Newer protocols address specific niches like enterprise use, speed, or storage.
Proof-of-Authority (PoA):
Relies on the reputation of pre-approved validators. It is highly scalable and common in private or consortium blockchains like VeChain.
Proof-of-History (PoH):
Used by Solana, it uses cryptographic timestamps to order transactions, allowing for massive throughput.
Proof-of-Capacity/Space (PoC):
Uses available hard drive space rather than computational power (e.g., Chia).
Proof-of-Burn (PoB):
Validators "burn" (destroy) tokens to gain mining power, demonstrating long-term commitment.
Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG):
Not a traditional block-based system; each new transaction confirms two previous ones, enabling high scalability without miners (e.g., IOTA, Nano).
4. 2025 Evolution:
Modular Blockchains:
Separating consensus from execution to improve speed (e.g., Celestia, Cosmos).
AI & Quantum State Protocols:
2025 research explores AI-enabled node selection and quantum-resistant consensus to future-proof networks against emerging threats.
