How Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Works
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) is one of the most revolutionary concepts to emerge from the blockchain and cryptocurrency space. It aims to transform the traditional financial system by replacing intermediaries such as banks and financial institutions with decentralized protocols and applications
Go Back
🕒 8:58 PM
📅 Jan 17, 2025
✍️ By SpurProtocol
In this article, we’ll explore how DeFi works, its core components, the benefits it offers, and its potential to disrupt the global financial system.
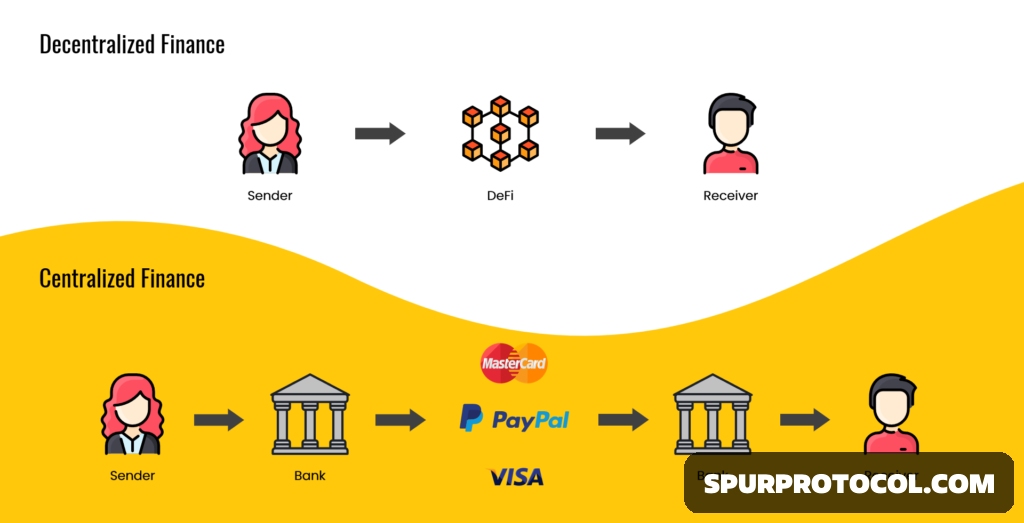
What is DeFi?
DeFi, short for decentralized finance, refers to financial services and products that are built on blockchain networks, particularly Ethereum. These services mimic traditional financial activities such as lending, borrowing, trading, and earning interest, but without relying on centralized intermediaries like banks or financial institutions.
The key feature of DeFi is decentralization. Instead of relying on a centralized authority, DeFi applications (often called dApps) operate on smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These smart contracts are stored on a blockchain, ensuring transparency, security, and immutability.
How Does DeFi Work?
DeFi platforms utilize several core components and technologies that make the ecosystem functional. Here’s a breakdown of how DeFi works:
1. Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are at the heart of DeFi applications. They allow users to enter into agreements and transactions without the need for a third party. These contracts are executed automatically when the agreed-upon conditions are met, reducing the risk of human error and manipulation. Smart contracts operate on blockchain platforms, with Ethereum being the most popular blockchain for DeFi projects.
2. Blockchain Technology
DeFi protocols are built on blockchain networks like Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain, and Solana. Blockchain provides a decentralized, immutable ledger that ensures transparency, security, and traceability of transactions. Each transaction or action on a DeFi platform is recorded on the blockchain, and once recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted.
3. Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
Traditional financial markets rely on centralized exchanges (CEXs) where users trade assets through an intermediary. DeFi replaces these centralized platforms with Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs), where users can trade directly with one another. DEXs facilitate peer-to-peer transactions by utilizing liquidity pools and automated market makers (AMMs). Examples of popular DEXs include Uniswap, SushiSwap, and PancakeSwap.
4. Liquidity Pools
In DeFi, liquidity pools are pools of assets provided by users to facilitate decentralized trading and lending. These pools are essential for the functioning of DEXs and other DeFi platforms. By providing liquidity, users can earn passive income in the form of trading fees, interest, or rewards. Liquidity providers are rewarded for supplying assets to these pools.
5. Stablecoins
Stablecoins are digital currencies pegged to the value of traditional assets like the US Dollar, Gold, or other fiat currencies. They are commonly used in DeFi platforms to reduce the volatility associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum. Popular stablecoins used in DeFi include USDT (Tether), USDC (USD Coin), and DAI.
6. Lending and Borrowing
One of the most popular DeFi use cases is lending and borrowing. Users can lend their crypto assets to others in exchange for interest, while borrowers can access loans without the need for credit checks or intermediaries. Platforms like Aave, Compound, and MakerDAO enable users to lend or borrow funds using cryptocurrencies as collateral.
7. Yield Farming and Staking
Yield farming and staking are two methods that allow DeFi users to earn rewards by participating in decentralized networks. In yield farming, users provide liquidity to DeFi platforms in exchange for returns, while staking involves locking up cryptocurrencies to help secure a blockchain network in return for staking rewards. Both methods aim to encourage user participation and liquidity provision.
Benefits of DeFi
- Accessibility: DeFi platforms are open to anyone with an internet connection, allowing individuals from all over the world, including those who are unbanked, to access financial services.
- Transparency: Since all transactions are recorded on the blockchain, DeFi provides greater transparency than traditional systems. Users can track transactions, verify balances, and monitor activities in real-time.
- Reduced Intermediaries: By eliminating intermediaries like banks and brokers, DeFi can reduce transaction fees and inefficiencies, making financial services more affordable and accessible.
- Control and Ownership: DeFi allows users to retain full control and ownership of their assets. Unlike traditional banking systems, users don't need to trust third parties to hold or manage their funds.
- Innovation: DeFi enables the creation of new financial products and services, such as decentralized insurance, synthetic assets, and prediction markets.
Risks and Challenges of DeFi
- Smart Contract Bugs: Although smart contracts are designed to be secure, flaws in the code can lead to vulnerabilities and exploits.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: DeFi operates in a largely unregulated space, and future regulatory changes could impact the viability and legality of certain DeFi protocols.
- Security Risks: As the DeFi ecosystem grows, so does the risk of hacking and fraudulent activities. Since the space is decentralized and often lacks traditional customer support channels, users are responsible for their own security.
- Volatility: DeFi assets and tokens can be highly volatile, leading to potential financial loss.
In Short
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) represents a paradigm shift in the financial industry. By leveraging blockchain technology, smart contracts, and decentralized applications, DeFi offers users greater control, transparency, and efficiency than traditional financial systems. Despite its potential, DeFi is still in its early stages and comes with risks that users should be aware of. As the DeFi space continues to evolve, it has the potential to reshape the global financial landscape and provide innovative financial solutions to a broader audience.
References:
