How Do Interest Rates Work Or Being Implemented In DeFi Protocols?
what are the concepts of interest rate in DeFi protocols.
Go Back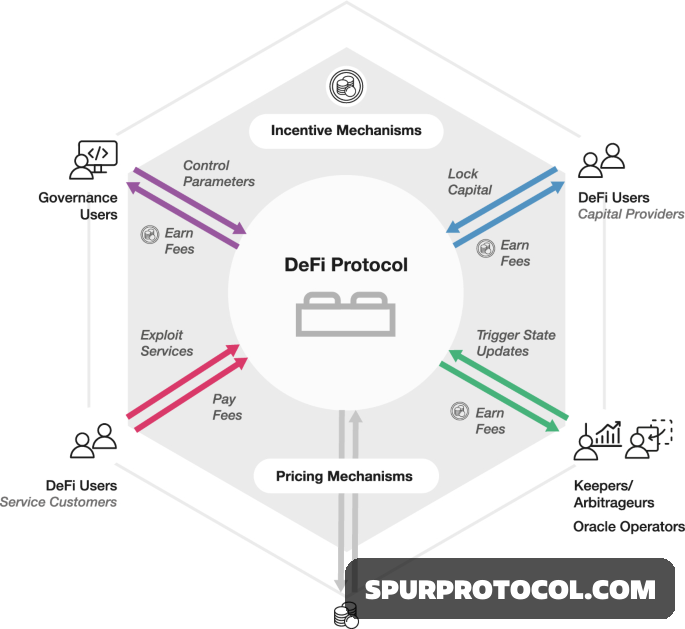
🕒 11:31 AM
📅 May 24, 2025
✍️ By oluwafemighty
what are the concepts of interest rate in DeFi protocols.
Go Back
🕒 11:31 AM
📅 May 24, 2025
✍️ By oluwafemighty
In DeFi, interest rates are typically determined algorithmically based on supply and demand within lending and borrowing protocols. Here's how they generally work:
1. Supply and Demand Model
1.Most DeFi protocols like Aave, Compound, and MakerDAO use dynamic interest rate models:
2. Supply Rate: Interest earned by lenders.
3. Borrow Rate: Interest paid by borrowers.
4. Utilization Rate: Ratio of borrowed assets to total supplied assets.
As utilization increases:
1. Borrow rates increase to discourage excessive borrowing.
2. Supply rates also increase to attract more lenders.
2. Interest Rate Curves:
1. Protocols use formulas or models (e.g. interest rate curves) to adjust rates
2. Low utilization → Low borrow/supply rates.
3. High utilization → Steep rise in borrow rates to prevent illiquidity.
Example (Compound’s model):
1. Borrow Rate = Base Rate + (Utilization * Multiplier).
2. Supply Rate = Borrow Rate * Utilization * (1 Reserve Factor)
3. Fixed vs Variable Rates:
1. Variable (Floating) Rates: Most common; adjust in real time.
2. Fixed Rates: Some protocols (e.g., Notional Finance) offer fixed rates using bond-like instruments or prediction mechanisms.
4. Interest Distribution:
1. Lenders earn interest continuously as borrowers pay interest.
2. Some protocols offer additional rewards (e.g. governance tokens) on top of interest, boosting effective yield (APY).
5. Yield Farming Impact:
Incentives from token rewards (e.g. COMP, AAVE) can temporarily distort interest rates, leading to unsustainable APYs in some cases.