How Does Zero-knowledge Proof (ZKP) Work?
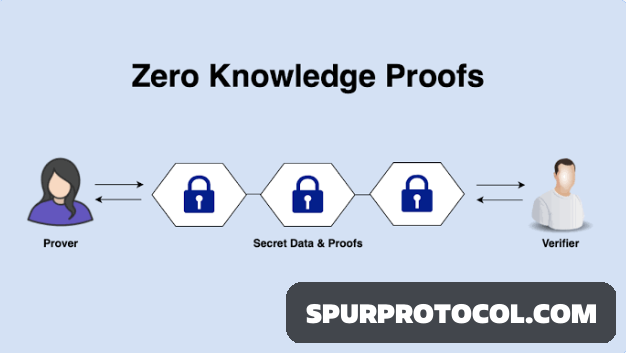
Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs) are cryptographic methods that allow one party (the prover) to prove to another party (the verifier) that a statement is true, without revealing any information about why it’s true or what the statement contains
Go Back
🕒 7:55 AM
📅 Jul 17, 2025
✍️ By prejworld
Here's a breakdown of how ZKPs work:
The Core Idea:
The prover has some secret information (a "witness") related to a public statement.
The prover wants to convince the verifier that they know this secret without revealing the secret itself.
A ZKP allows the prover to generate a proof, which the verifier can check to confirm the statement's truthfulness without learning anything about the secret.
Key Properties:
Completeness:
If the statement is true, an honest prover can always convince an honest verifier.
Soundness:
If the statement is false, a dishonest prover cannot convince an honest verifier except with negligible probability.
Zero-Knowledge:
If the statement is true, the verifier learns nothing beyond the fact that the statement is true.
How it Works (Simplified Example):
Imagine a tunnel with a locked door and a secret code. The prover knows the code.
The verifier wants to know if the prover knows the code, but doesn't want the code itself.
The prover can walk through the tunnel (entering from one side and exiting from the other). The verifier can watch this, and be convinced the prover knows the code, without learning the code itself.
In this analogy, the tunnel represents the ZKP protocol, the locked door represents the statement, and the secret code represents the witness.
Types of ZKPs:
Interactive: Involve a back-and-forth communication between the prover and verifier.
Non-Interactive: The prover generates a proof that can be verified later without further interaction with the verifier.
Applications:
Authentication: Verifying identity without revealing personal information.
Voting Systems: Ensuring secure and anonymous voting.
Privacy-Preserving Location Services: Proving location without revealing exact coordinates.
Blockchain Scalability: zk-Rollups use ZKPs to improve transaction processing efficiency.
Access Control: Managing access to resources without revealing sensitive data.
