HOW LIQUIDITY POOLS WORK IN CRYPTO
A liquidity pool is a collection of cryptocurrency tokens locked in a smart contract, used to facilitate trading on decentralized exchanges (DEXs)
Go Back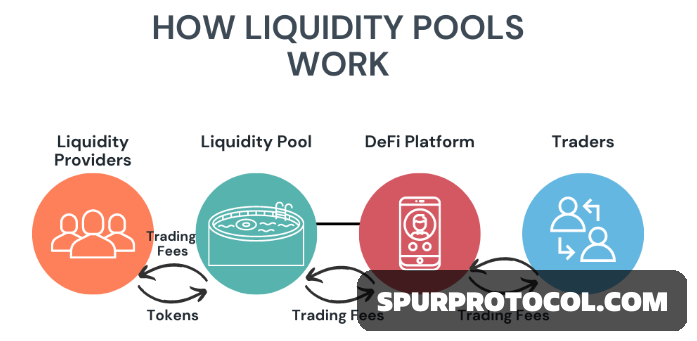
🕒 6:26 AM
📅 Nov 23, 2025
✍️ By Iceprince
A liquidity pool is a collection of cryptocurrency tokens locked in a smart contract, used to facilitate trading on decentralized exchanges (DEXs)
Go Back
🕒 6:26 AM
📅 Nov 23, 2025
✍️ By Iceprince
Instead of a traditional order book, these pools use an Automated Market Maker (AMM) to automatically determine asset prices and execute trades. Users who deposit assets into a pool are called liquidity providers (LPs) and are rewarded with a portion of the trading fees.
How it works
1. Token pairs: A liquidity pool consists of a pair of tokens, such as ETH/USDC. To provide liquidity, users must deposit equal values of both tokens into the pool.
2. Automated Market Maker (AMM): A smart contract uses a mathematical formula, like the constant product formula (x*y=k) used by Uniswap, to determine the price of the tokens based on the ratio of assets in the pool.
3. Decentralized trading: When a user wants to swap one token for another, they interact with the pool's smart contract. The AMM executes the trade by taking one token from the pool and giving back the other, at the price determined by the formula.
4. Liquidity providers: Users who contribute assets to a pool are called liquidity providers (LPs). In return for providing capital, they receive liquidity pool tokens that represent their share of the pool.
5. Earning fees: LPs earn passive income by receiving a share of the fees from every trade that is executed using their pool.
Benefits and risks
Benefits: Liquidity pools allow for 24/7, automated, and permissionless trading on DEXs, without intermediaries. They also provide a way for users to earn passive income.
Risks: There are risks involved, such as impermanent loss, which occurs when the price of the deposited assets changes significantly. There is also the risk of smart contract vulnerabilities, where bugs in the code could lead to a loss of funds.