LAYER 2 SOLUTIONS IN BLOCKCHAIN
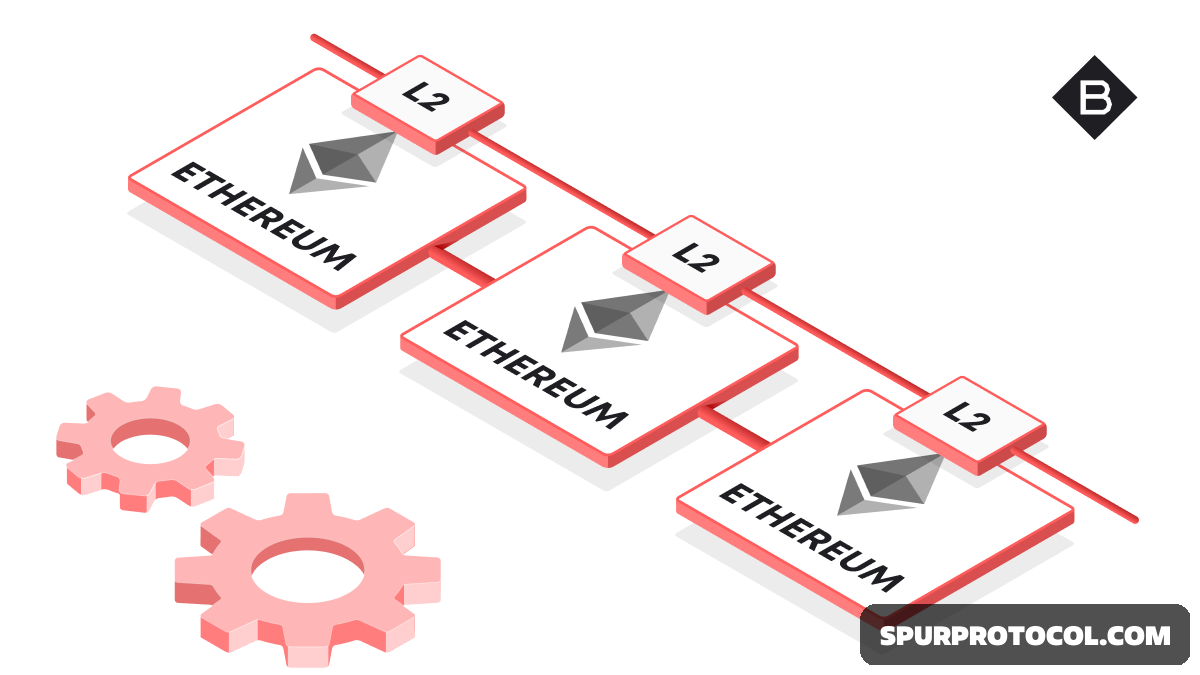
Layer 2 (L2) solutions are protocols built on top of existing Layer 1 (L1) blockchains (like Ethereum) to improve scalability, speed, and reduce transaction costs by processing transactions off-chain while still leveraging the security of the base L1 network.
Go Back
🕒 7:30 PM
📅 Oct 15, 2025
✍️ By chyneyz
Key mechanisms include state channels, sidechains, and particularly rollups (Optimistic and Zero-Knowledge Rollups), which bundle multiple transactions and submit them to the L1 chain for final verification.
How Layer 2 Solutions Work
Off-Chain Processing:
Most transactions are handled by the L2 protocol, which operates separately from the main blockchain.
☆ Bundling:
Multiple off-chain transactions are grouped together into a single transaction.
☆ Anchoring to L1:
The summarized data or proof of these transactions is then sent back to the Layer 1 blockchain for final validation and permanent storage, ensuring security and data integrity.
☆ Inherited Security:
L2 solutions do not replace the L1's security but rather rely on it for their own security guarantees.
Types of Layer 2 Solutions
☆ Rollups:
This is a popular category that processes transactions off-chain and posts the transaction data onto the L1 chain.
☆ Optimistic Rollups:
Assume transactions are valid by default and only require a challenge period for fraud to be proven.
☆ ZK-Rollups:
Use zero-knowledge proofs to cryptographically verify transaction validity without revealing the transaction data itself, offering strong security.
☆ State Channels:
Allow parties to conduct numerous transactions off-chain and only record the final state on the main blockchain.
☆ Sidechains:
Independent blockchains that are pegged to a mainchain, allowing assets to move between them.
☆ Plasma Chains:
A type of L2 that creates secondary, smaller chains to handle transactions off-chain, using smart contracts and Merkle trees for efficiency.
Why Layer 2 Solutions are Important
☆ Increased Throughput:
Significantly increases the number of transactions a blockchain can process.
☆ Reduced Costs:
Lowers transaction fees by offloading processing from the congested main chain.
☆ Enhanced Speed:
Faster transaction confirmations by processing most activity off-chain.
☆ Improved Scalability:
Makes decentralized applications and blockchain networks more practical for wider adoption.
