Multi-Signature Wallets Explained
Multi-signature (multi-sig) wallets play a crucial role in Web3 security by requiring multiple approvals for transactions. This article will walk you through the basics of multi-sig wallets, their advantages, and how to use them to protect your digital assets.
Go Back
🕒 9:04 AM
📅 May 23, 2025
✍️ By ethangeorge
Introduction to Multi-Signature Wallets
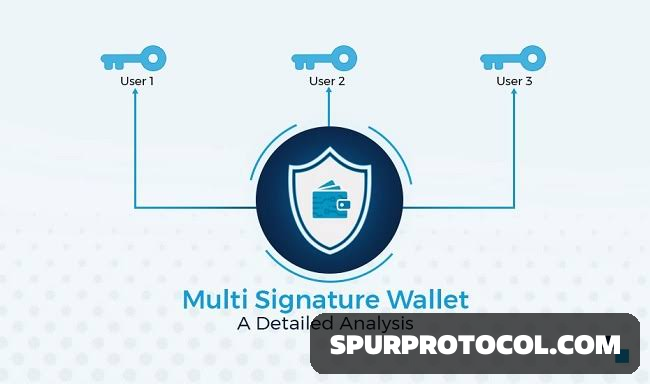
Multi-signature wallets require more than one private key to authorize a transaction, making them more secure than single-key wallets. They are especially useful for organizations or individuals who want extra layers of security and control over their assets.
Now let's talk about how they work.
How Multi-Sig Wallets Work
A multi-sig wallet needs multiple approvals (signatures) from designated participants to complete a transaction. For instance, a 2-of-3 wallet setup means any two of the three authorized parties must sign off to authorize a transaction. This setup prevents a single point of failure and reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
Use Cases for Multi-Sig Wallets
Multi-sig wallets are commonly used in:
- Business Operations: Shared control over funds within a team or organization.
- DeFi and DAOs: Enhanced security for community-managed funds.
- Personal Security: Extra protection for individuals managing large amounts of assets.
Setting Up a Multi-Sig Wallet
To set up a multi-sig wallet, choose a compatible platform (e.g., Gnosis Safe, Coinbase Wallet), define the number of authorized signers, and set the required number of signatures. Follow platform-specific instructions to complete the setup and familiarize yourself with adding or removing signers as needed.
Benefits and Drawbacks
- Benefits: Increased security, reduced risk of unauthorized transactions, and suitable for both personal and organizational use.
- Drawbacks: More complex to manage and less flexible if urgent action is required, as multiple approvals are necessary.
Using Multi-Sig Wallets Safely
To maximize security, ensure:
Each signer uses unique, secure devices.
Regular reviews of the signers and transaction policies.
Backup plans if one or more signers lose access to their private keys.
