The Power Of Hashing
Hashing is a very important technique used in many day to day digital functions, yet at the same time, it is often hidden away from the user. This article seeks to explain what Hashing is, and demonstrate its importance.
Go Back
🕒 10:22 AM
📅 May 23, 2025
✍️ By ethangeorge
What Are Hashes?
Hashing is the action of converting a certain input into a string of numbers and letters of a fixed length. This is commonly used for cybersecurity purposes, as well blockchain validations. It often works as a cryptography method.
How Does It Work?
To turn inputs into hashes, hashing algorithms are used. To prevent the original input from being decyphered, hash algorithms are one way only. For purposes of this quest, hash tables will not be focused on: however, if interested, more about hash tables can be read up in the above link.
Some Applications For Hashing
Hashing has numerous applications. One such application would be that of password storage. Compared to plain text storage, if the backend of a website was to be compromised and its database of passwords leaked out, the attacker would only get a hashcode that can’t be deciphered, ensuring the passwords are not compromised.
More Applications For Hashing
Another usage for hashing is confirming data integrity. Since different inputs result in different hashcodes, the received data can be run through a hashing algorithm to compare with the correct hashcode: if the two match, then the received data is correct.
Hashing and Antiviruses
Some malware detection work the same way: known malware have their hashcode taken, and when scanning for potential viruses, scanned items will have hashcodes created of them for comparison.
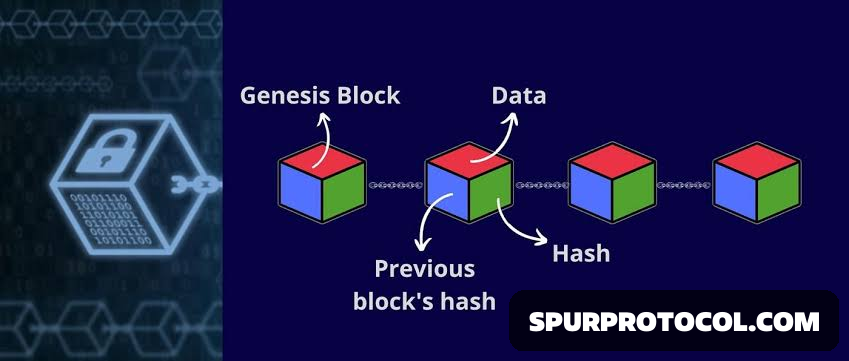
Usages For Blockchains
Hashing is imperative for blockchain technology as well. Everytime a new transaction is made, a new block is added to the blockchain: to ensure the transaction is a legitimate one and not a fabricated transaction made by attackers, hashing is used.
Specifics For Blockchain Hashing
First, the header of the previous transaction is hashed and then compared to the provided hashcode of said transaction. Once its proven the hashcode is the same, meaning no tampering has occurred, the current block is added to the chain and put through the hashing algorithm, thus repeating the cycle. This is why blockchains such as Bitcoin consume so much power when being mined: these algorithms can often be difficult to solve.
Have you learnt something today?
