What Is A DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) In Blockchain?
A DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) in blockchain is a data structure used as an alternative to the traditional blockchain architecture.
Go Back
🕒 7:49 AM
📅 Jul 17, 2025
✍️ By prejworld
Instead of organizing data in a linear chain of blocks, a DAG arranges transactions in a graph format where each transaction can point to (or approve) previous ones, and there are no cycles—meaning you can’t loop back to a previous transaction.
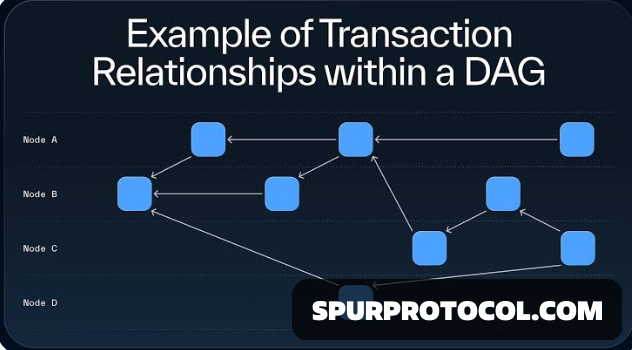
What is a DAG?
Directed:
Edges (connections) between nodes have a direction, indicating a flow of information or dependency.
Acyclic:
There are no cycles in the graph, meaning you can't start at a node and follow edges to return to that same node.
Graph:
Transactions are represented as nodes, and their relationships are depicted as edges.
How DAGs differ from Blockchains in Cryptocurrency:
Linear vs. Graph:
Blockchains link transactions sequentially in blocks, forming a chain. DAGs, on the other hand, link transactions directly, creating a more web-like structure.
Parallel Processing:
In DAGs, transactions can be processed concurrently, as they don't have to wait for previous blocks to be mined. This can lead to faster transaction speeds and higher throughput.
Consensus:
Blockchains rely on a single chain consensus mechanism. DAGs can utilize various consensus mechanisms, including those that allow for faster, more flexible transaction validation.
Advantages of DAGs in Cryptocurrency:
Faster Transactions:
Parallel processing of transactions can result in quicker confirmation times.
Lower Fees:
The ability to process transactions without the need for block creation can lead to reduced transaction fees.
Scalability:
DAGs are often more scalable than blockchains, particularly in high-transaction volume scenarios.
Real-time Data Availability:
DAGs can facilitate real-time data availability, making them suitable for applications like IoT and supply chain management.
Examples:
IOTA: Uses the Tangle, a DAG-based distributed ledger, for IoT devices.
Nano: Operates on a DAG-based "block-lattice" structure.
Hedera Hashgraph: Utilizes a DAG-based distributed ledger for fast, low-cost transactions.

