What Is A Full Node?
Full node is a computer that fully implements the rules of an underlying blockchain network and completely validates transactions and blocks on a blockchain.
Go Back
🕒 6:41 PM
📅 May 12, 2025
✍️ By Ecojames
What Is a Full Node?
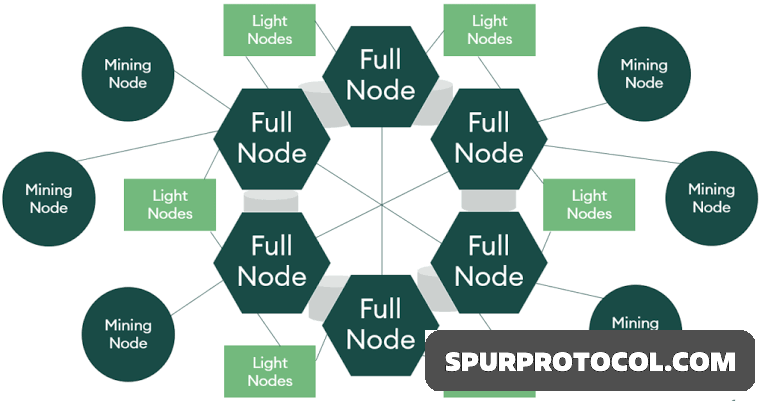
A full node is an integral component of any blockchain. It is a computer in a network of connected computers which validate and store transactions on a blockchain. It hosts a copy of the data on the entire blockchain and uses this information to verify the history of a transaction before validating any new data.
Types of Full Nodes:
A full node contains and maintains the entire translation data on a blockchain. Hence, a blockchain full node is considered a server in a traditional setting, which relays information on demand.
- The most important attribute of a full node is that they are a part of the blockchain governing model. This means that a blockchain can undergo improvements or upgrades only after a majority of full nodes agree to it.
- Full nodes have the strongest voting power on a blockchain of all types of nodes.
Full nodes are of two types, archival nodes and pruned nodes.
1. Archival Nodes:
Archival nodes maintain the entire blockchain in their database, and these are the type of full nodes found most commonly on a blockchain. The significant difference between archival and pruned nodes is the availability of memory.
Various types of archival nodes are miner nodes, masternodes, staking nodes, and authority nodes.
(a.) Miner nodes
Miner nodes are predominantly used in Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanism that often needs higher energy consumption and computational power to perform complex mathematical computations to validate transactions.
(b.) Masternodes
Masternodes only validate transactions and maintain the blockchain ledger but do not have the authority to add new blocks to the blockchain.
(C.) Staking Nodes
Staking nodes are primarily used in the proof-of-stake consensus mechanism where staking is involved. Using staking nodes, users can stake money, validate transactions, and avail rewards.
(d. ) . Authority Nodes
Authority nodes authorize other nodes from joining a blockchain network, allowing or disallowing access to the rest of the nodes. However, this authority is limited to only a hand full of authority nodes in a private blockchain and some partially-centralized blockchains.
2. Pruned Nodes:
Pruned full nodes have limited space to hold data. They download the blocks to maintain the ledger but delete the oldest block and make space for the latest downloaded block. That said, older blocks are not completely deleted, but their vital metadata is preserved to maintain the fundamental principles of blockchain.
Benefits of Running a Full Node
1. Support decentralization
A constant audit that verifies transactions independently, guarding the blockchain against fraud or tampering.
2. Network security impact
Nodes rigorously enforce Bitcoin’s consensus rules. This role directly protects the network’s integrity.
3. Boost privacy
Broadcasting transactions directly from a full node reduces reliance on external servers, limiting third-party surveillance and protecting node operators’ privacy.

