What Is An Order Book And How Does It Work?
Order books display the current buy and sell orders(bids and asks) showing the market's supply and demand dynamics for a given trading pair.
Go Back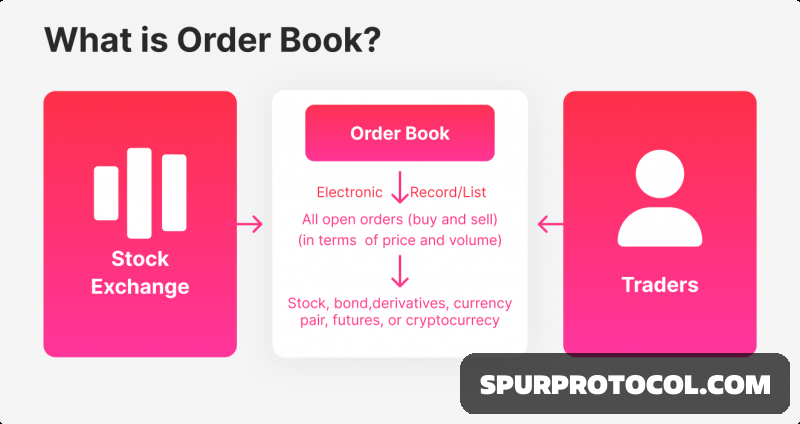
🕒 7:45 PM
📅 Apr 04, 2025
✍️ By Ecojames
Order books display the current buy and sell orders(bids and asks) showing the market's supply and demand dynamics for a given trading pair.
Go Back
🕒 7:45 PM
📅 Apr 04, 2025
✍️ By Ecojames
An order book is like a real-time list of all the current buy and sell orders for a particular assets such as stocks, commodities or cryptocurrencies.
Types of Orders
There are several types of orders that traders can place into an order book, each serving specific needs and strategies.
1. Market Orders
This is a directive given by traders to buy or sell a security at the best available current market price.
2. Limit Orders
A limit order is a directive to buy or sell a security at a specific price or better. For example, a buy limit order could be set at the current market price or lower, and a sell limit order could be placed at the current market price or higher.
3. Stop Orders
Also known as a ‘stop-loss’ order, this is an order to buy or sell a stock once the price reaches a specific trigger point, intending to limit an investor’s potential loss.
How Order Books Work
At their core, order books function as the operational backbone of any financial marketplace, facilitating transactions and fostering market transparency.
1.The Essence of Matching Orders
The order book’s primary function revolves around order matching, a process guided by a set of sophisticated algorithms. As the name suggests, order matching involves pairing a buy order with a corresponding sell order.
-To elaborate, let’s assume a trader places a market order to sell 50 shares of Company A. The order book algorithm scans the book for the highest buy order that can fulfill this request. Suppose the best bid at that moment is for 25 shares at $50 each. The algorithm will execute this part of the sell order at $50 per share. If the next best bid is for 38 shares at $49, the algorithm will sell the remaining 25 shares at $49 per share. This dynamic process ensures that market orders are filled at the best possible price at any given time.
2.Depth and Spread – Two Sides of the Same Coin
Two key indicators of a security’s status in an order book are its depth—the volume of open buy and sell orders—and the spread between the highest bid and the lowest ask price.
-For instance, a narrow spread (a small difference between the bid and ask prices) coupled with significant depth at these levels usually suggests a highly liquid market with healthy competition among traders, thereby minimizing the cost of trading. On the other hand, a wide spread coupled with low depth could indicate lower liquidity and higher volatility, leading to potentially higher trading costs.
3.Price-Time Priority Rule
A cardinal rule guiding the operation of order books is the Price-Time Priority rule. This rule means that the order with the highest bid (for buyers) or the lowest ask (for sellers) gets filled first. If two orders have the same price, the one placed earlier gets priority.
4.The Real-Time Nature of Order Books
Order books function in real-time, continually updating to reflect the current state of the market. This dynamic nature is fundamental to their role in the marketplace, ensuring that traders have access to the most current information.