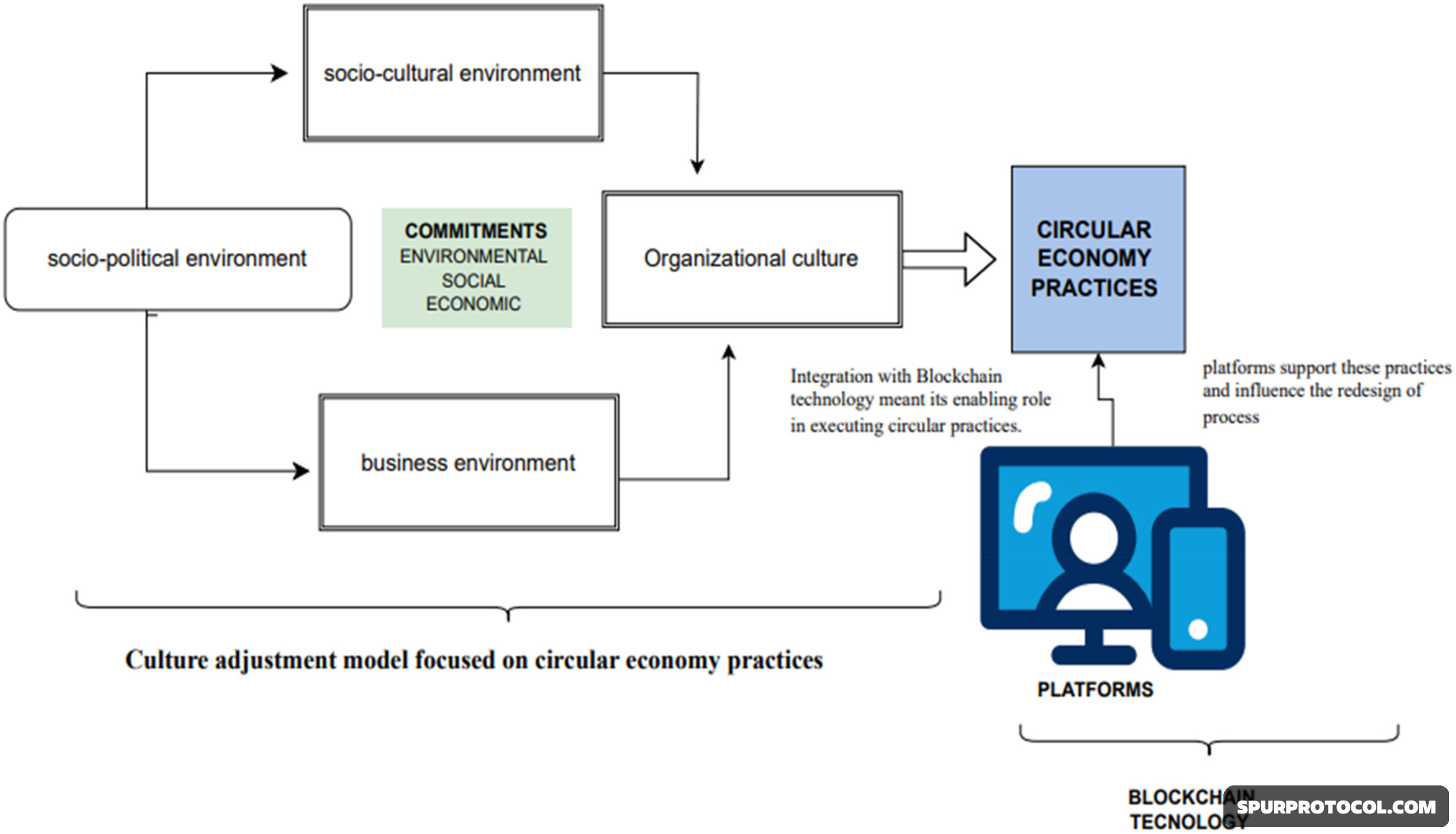
Key roles of blockchain in a circular economy👇
Product and material traceability:
A blockchain can track a product's journey from creation to end-of-life, including the sourcing of its components, a process that is often opaque in traditional supply chains.
Verifying circularity:
It provides a tamper-proof record that can certify the recycling paths of materials, assuring consumers of a product's sustainability claims and allowing for the creation of digital "green passports" for goods, notes Circuloos and the Ellen MacArthur Foundation.
Enabling new business models:
By providing a secure and verifiable record, blockchain facilitates new models like shared ownership, refurbishment, and resale markets, as it can assign a financial value to reused components.
Incentivizing sustainable behavior:
It can underpin incentive programs, rewarding consumers for returning products for recycling or for extending a product's life through repair.
Improving supply chain efficiency:
It builds trust and transparency among different supply chain actors, which helps to reduce inefficiencies and miscommunication in managing the flow of materials.