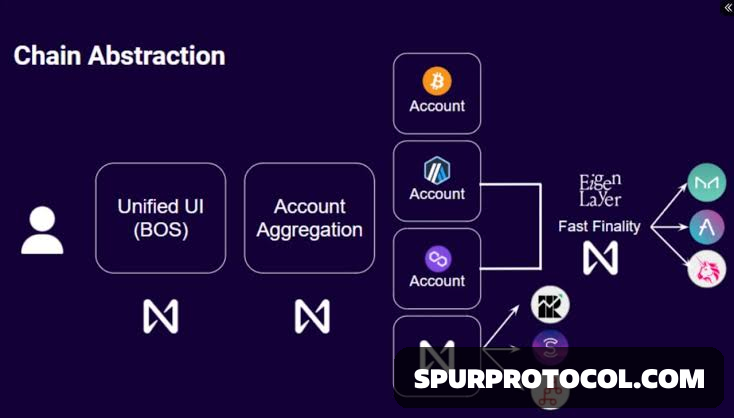
What Is Chain Abstraction?
Chain abstraction is NEAR’s idea of simplifying how users interact with blockchain technology by separating it from the user experience (UX).
How Does Chain Abstraction Work?
1.Efficiency
Users should be able to interact with decentralized applications (DApps) across different blockchains without unnecessary hurdles.
The goal of chain abstraction is to remove or hide the complexities of blockchain technology, allowing users to focus on the functionality and benefits of the DApps they use. For instance, if Kahenya wants to use a new DApp called XYZ, he should not have to worry about which blockchain it is built on. From a user perspective, he just wants it to work well and fulfill its purpose.
2.Transactions
Imagine using a DApp that allows you to easily transact across multiple networks and navigate different services. For instance, imagine that Kahenya opens the XYZ app on his phone, orders a coffee, and sees a discount for his favorite clothing store. He buys a pair of shoes, earning rewards that are stored as non-fungible tokens (NFTs) on Ethereum. Later, he notices a special offer tied to his reward and buys tickets to an event, which are also NFTs, but on BNB Smart Chain (BSC).
-All these transactions could happen in a single app, removing the need for Kahenya to manage multiple wallets, switch networks, or directly handle transaction fees. This level of cross-chain interaction is the ultimate goal of chain abstraction.
Benefits of Chain Abstraction
1.Defragmenting liquidity
Liquidity is often isolated within specific blockchains, making it difficult for users and developers to access and use it. Chain abstraction addresses this by enabling access to liquidity across various blockchains.
Imagine that Augustus wants to lend his tokens to earn interest. If liquidity is isolated, he would need to find a platform on the specific blockchain his tokens are on. However, with chain abstraction, Augustus could lend his tokens on a platform that integrates liquidity from multiple blockchains. This may result in more users for the platform and more competitive interest rates for Augustus.
2.Simplified development
For developers, chain abstraction offers the flexibility to build DApps without being limited to the constraints of a specific blockchain.
A developer might use Ethereum for its smart contract capabilities while utilizing Polygon for its cost efficiency. For instance, Decentraland uses the Polygon network to allow its users to claim, buy, sell, and trade wearables for their avatars with no transaction fees. It’s important to note that Decentraland utilizes multiple features to completely remove the fees. Transactions in Polygon have small fees but are not entirely free.
Challenges of Chain Abstraction
1.Centralization risks
Chain abstraction could be implemented through the creation of an interface that would allow users to interact with all kinds of blockchain applications from a single place, enhancing user experience. However, there is a concern that this interface may potentially become a single point of failure.
2.Security risks
Each blockchain has its own security protocols. If they are combined into a single interface, ensuring that all security measures are upheld is challenging. If not implemented carefully, the new interface of chain abstraction could bring risks to individual blockchains.
3.Interoperability issues
Ensuring interoperability across various blockchains is another challenge. Different blockchains have unique consensus algorithms and smart contract languages, making it difficult to create a single interface that works flawlessly across all networks. For instance, a smart contract written for the Ethereum network is not directly compatible with Solana due to differences in their programming language and underlying technology.
Common Misconceptions About Chain Abstraction
1.Chain abstraction eliminates blockchain differences
While chain abstraction involves simplifying cross-chain interactions, each blockchain's unique features remain intact. Chain abstraction simplifies and automates the technical processes to improve user experience but does not directly change the blockchain infrastructures.
2.Chain abstraction is only about cross-chain transactions
Facilitating transactions across different blockchains is a significant feature of chain abstraction, but not its only utility. Chain abstraction also involves simplifying the use of DApps, deployment of smart contracts, and data retrieval across blockchains.