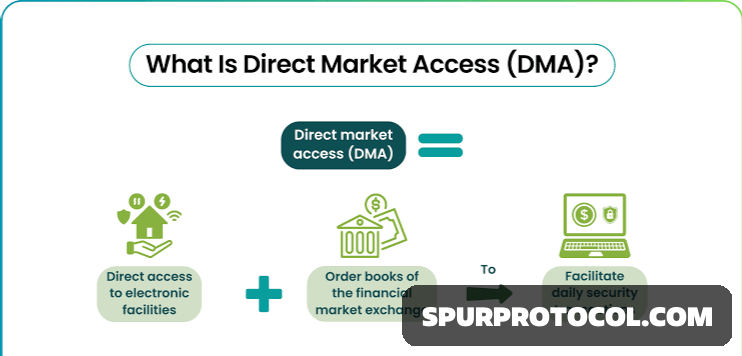
What Is Direct Market Access (DMA)?
Direct market access is a technology that provides investors direct access to order books without the need for brokers.
Go Back
🕒 6:41 PM
📅 May 10, 2025
✍️ By Ecojames
Direct market access (DMA) trading is the process of placing orders directly with an exchange. DMA trading is available for a variety of financial instruments, including stocks and forex.
How are Trades Executed in Direct Market Access?
1. Through an online trading platform, a trader places an order to purchase a security.
2. The order is then recorded in an electronic trading book, and information is communicated to exchange servers.
3. The order is received by the stock exchange, and it can be fulfilled once the trader’s purchase price matches a seller’s price.
Advantages of Direct Market Access
1. Since there is no longer a broker involved in the trading process, the investor can get access to the market faster, which reduces transaction costs and increases the speed of which the transactions are executed.
2. Transactions are managed by the investor instead of a broker, so the former will exert more control over the trade order(s).
3. The investor gets the opportunity to take part in pre-market and post-market auctions.
4. There are low risks of the investor’s confidential information getting leaked, as there are no third-party vendors involved, and trading takes place anonymously.
5. The investor can get access to high-frequency trading, which is a type of algorithmic trading technique that utilizes high-frequency data and trading tools to produce high speed and high turnover rate.
Disadvantages of Direct Market Access
1. It requires the use of sophisticated technology infrastructure to get direct access to stock exchanges and enable electronic trading. Therefore, it can be costly for businesses to maintain.
2. If there are issues with internet connectivity, it may impact the connection to direct market access.
3. It is significantly regulated to ensure that trades are executed properly. It means that trading will be less flexible compared to over-the-counter methods.
4. If the investor’s trading account becomes inactive or if they do not trade very often, penalty fees will apply.

