What Is Finality In Blockchain?
what does the word Finality mean in blockchain?.
Go Back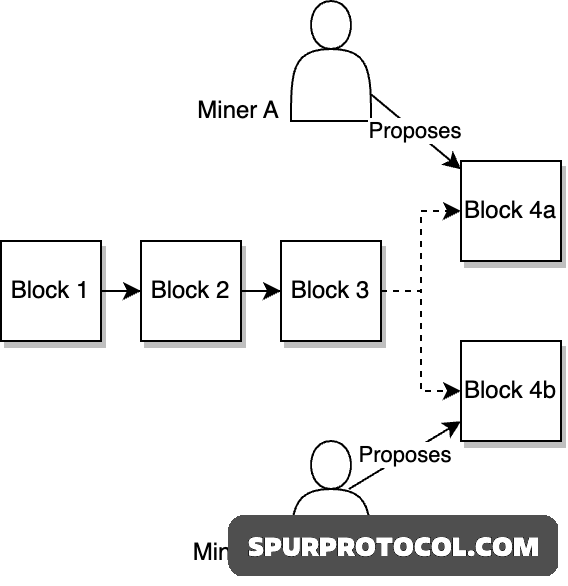
🕒 5:53 PM
📅 May 14, 2025
✍️ By oluwafemighty
what does the word Finality mean in blockchain?.
Go Back
🕒 5:53 PM
📅 May 14, 2025
✍️ By oluwafemighty
Finality in blockchain refers to the point at which a transaction is considered irreversible and permanently part of the blockchain. Once a transaction has finality, it cannot be changed, canceled, or double-spent it’s guaranteed to be part of the canonical chain
There are two main types of finality:
1. Probabilistic Finality:
i). Used in blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum (pre-Merge).
ii). A transaction becomes more "final" as more blocks are added on top of it.
There's always a small chance of a chain reorganization, so finality is not 100% guaranteed, but becomes extremely unlikely over time (e.g., 6 confirmations in Bitcoin is generally considered final).
Deterministic (or Absolute) Finality:
1. Used in proof of stake systems with Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) algorithms (e.g., Ethereum 2.0, Tendermint, Polkadot).
2. Once validators agree and finalize a block, it’s impossible to reverse without significant validator misbehavior (usually with slashing penalties).
3. Finality is instant and guaranteed once reached.
Irreversible Confirmation:
Finality signifies that a transaction has been successfully validated and confirmed by the blockchain network, making it impossible to reverse or change.
Guaranteed Security:
The finality of transactions is a critical aspect of the security and reliability of blockchain systems, as it prevents fraudulent activities or disputes over the validity of a transaction.
Consensus Mechanisms:
Finality is achieved through consensus mechanisms like Proof-of-Work (PoW) or Proof-of-Stake (PoS), which involve a network of validators reaching agreement on the validity of a transaction before it's added to the blockchain.
Probabilistic vs. Deterministic Finality:
Some blockchains offer probabilistic finality, where the likelihood of a transaction being reversed decreases as more blocks are added to the chain, while others provide deterministic finality, offering an immediate guarantee of permanence.
Foundation for Trust:
Finality plays a vital role in building trust and confidence in blockchain technology, as it assures users that their transactions are secure and irreversible.
I hope you learn something new
Good luck 🫶