What Is Formal Verification Of Smart Contracts
Formal verification of smart contracts is a rigorous, mathematical method used to prove that a smart contract's code is correct, secure, and free from bugs and vulnerabilities, ensuring it behaves exactly as intended under all possible scenarios.
Go Back
🕒 8:51 PM
📅 Dec 15, 2025
✍️ By chyneyz
How it Works
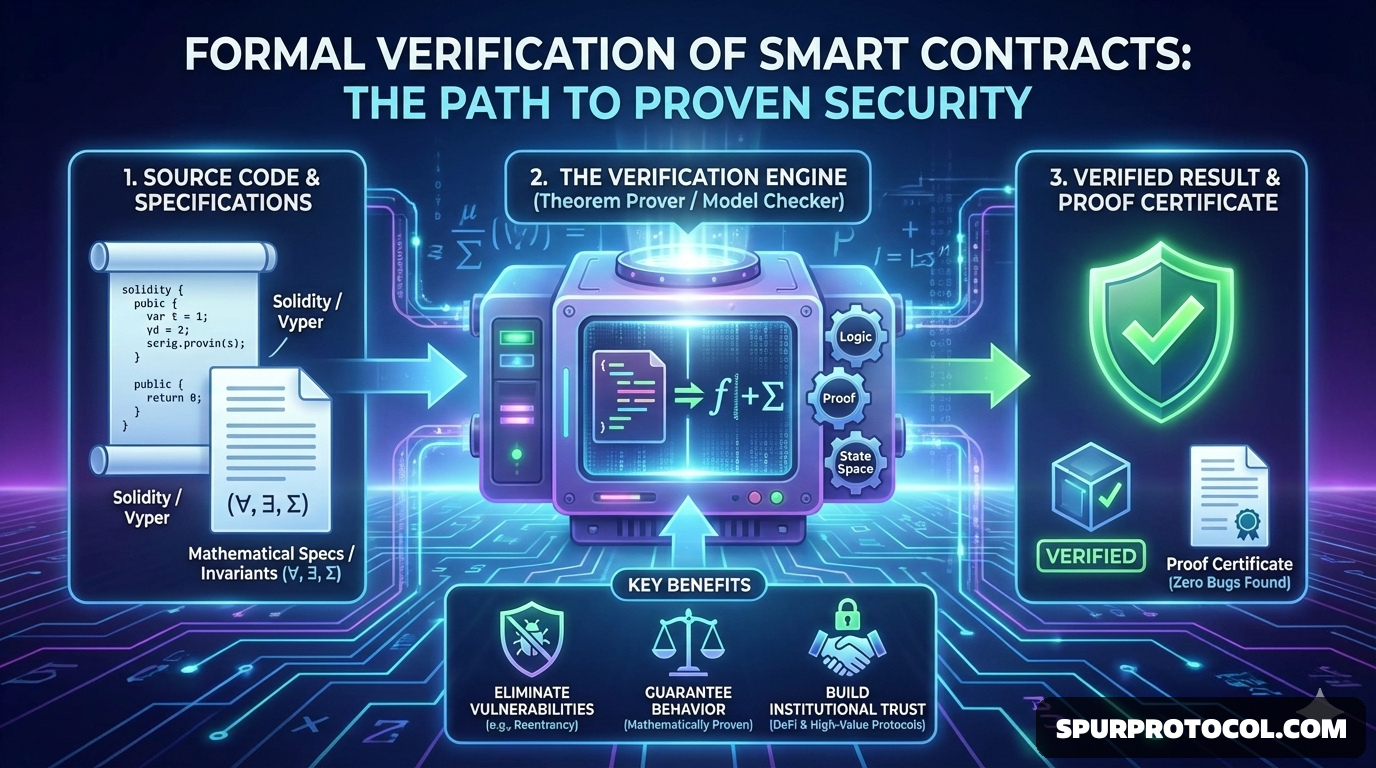
The process involves several key steps:
Formal Specification:
The desired behavior, security requirements, and invariants (conditions that must always be true, such as the total token supply remaining constant) of the smart contract are precisely defined in a formal, mathematical language. A clear and unambiguous specification is crucial, as the entire process depends on its quality.
Mathematical Modeling:
The smart
contract's actual source code or bytecode is translated into an abstract mathematical model (such as a finite-state machine) that captures its logic and behavior.
Proof and Analysis:
Specialized automated tools, such as theorem provers and model checkers, are used to mathematically prove that the model satisfies all the properties outlined in the formal specification.
Counterexample Analysis (if needed):
If a property is violated, the tool generates a counterexample—a specific sequence of transactions and inputs that demonstrates the flaw. Developers then use this information to fix the bug, and the process is repeated.
Key Benefits
Highest Assurance:
It offers a mathematical proof of correctness, providing the strongest possible security guarantee.
Early Bug Detection:
It uncovers subtle, hard-to-find logical errors and edge-case vulnerabilities (like reentrancy attacks or integer overflows) before deployment, which often evade manual audits and traditional testing.
Prevents Catastrophic Losses:
Given that smart contracts often manage billions in assets and are immutable once deployed, catching critical flaws prevents massive, irreversible financial losses.
Enhanced Trust:
Using formal verification demonstrates a commitment to security, building significant user and investor confidence.
Challenges:
Complexity and Expertise:
Writing accurate formal specifications and operating the verification tools requires specialized knowledge and significant expertise in mathematics and formal logic
.
Resource Intensive:
The process can be computationally intensive and time-consuming, especially for complex contracts.
Specification Quality:
The effectiveness of formal verification depends entirely on the quality of the specifications; a poorly defined specification can lead to undetected bugs.
Formal verification is a powerful layer of a comprehensive security strategy, complementing manual audits and traditional testing to ensure maximum security for high-value smart contracts.
Why This Matter:
Unlike traditional testing, which only shows the presence of bugs for specific inputs, formal verification provides a mathematical guarantee of their absence for the verified properties.
