What Is Merkle Proof And Its Function In Light Clients?
A Merkle Proof is a cryptographic verification method that allows a user to confirm the inclusion of a specific transaction within a block, using only the block's single cryptographic summary (the Merkle Root) and a short proof. This enables light clients to verify transactions securely without downloading the entire blockchain.
Go Back
🕒 8:46 AM
📅 Nov 04, 2025
✍️ By Nathanael707
Defining Merkle Proof and Merkle Root
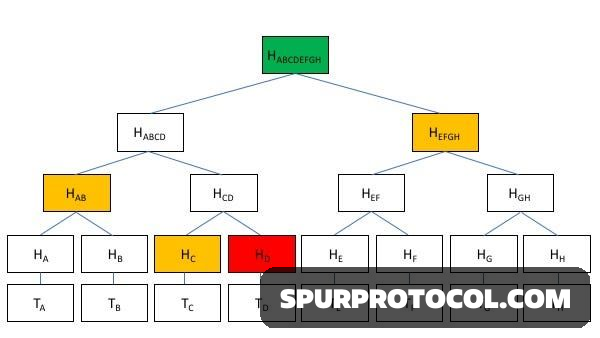
A Merkle Tree summarizes all transactions in a block into a single hash, the Merkle Root, found in the block header. The Merkle Proof is the short path of hashes needed to verify a single transaction's place in that tree.
- Merkle Root: The single cryptographic fingerprint representing all transactions in a block.
- Merkle Proof: The small set of intermediate hashes required to trace a transaction's path up to the Merkle Root.
The Role in Simple Payment Verification (SPV)
Merkle Proofs are the backbone of Simple Payment Verification (SPV), a technique crucial for mobile wallets.
- Light Client Efficiency: Light clients only download block headers (which contain the Merkle Root).
- Verification: To check a transaction, the client receives the Merkle Proof and cryptographically verifies that the transaction is correctly included in the root, without needing the full block data.
