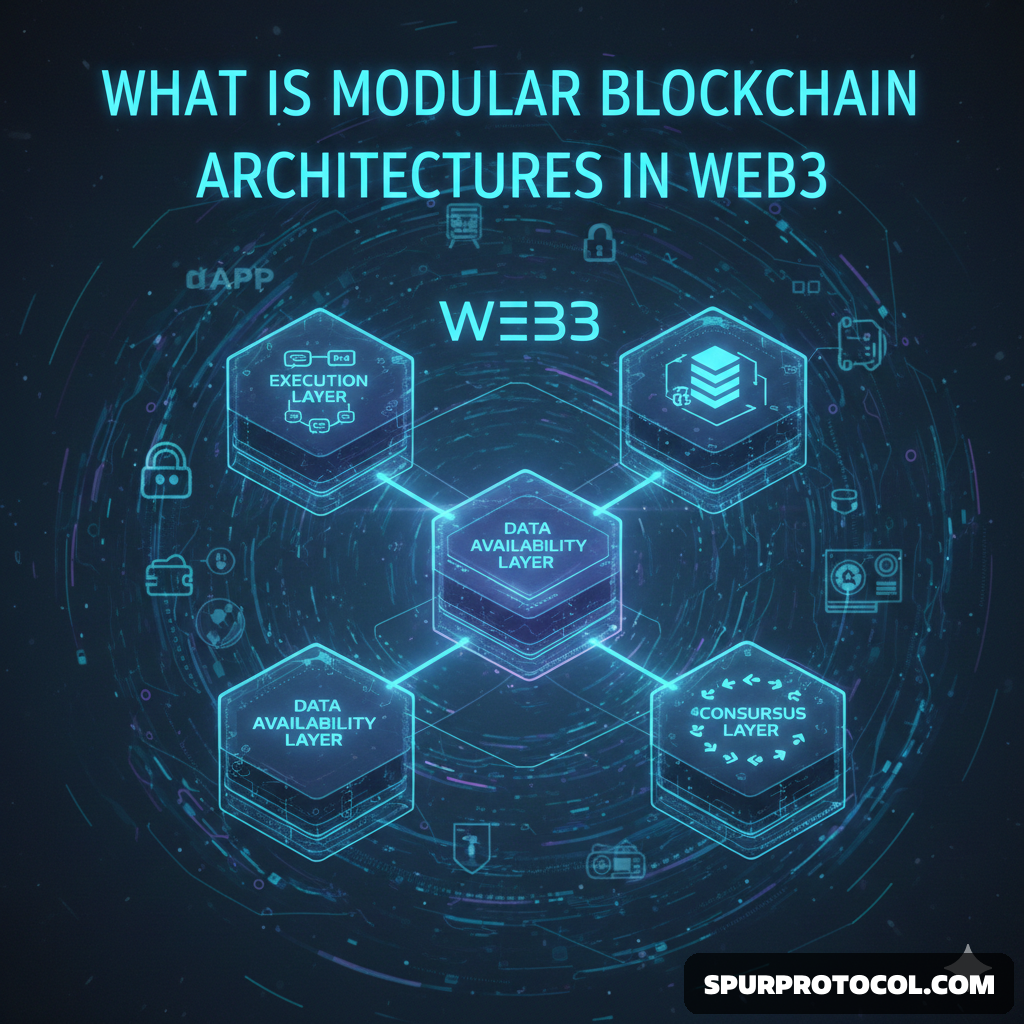
Execution Layer: Processes transactions and smart contracts (e.g., Optimism, Arbitrum).
Consensus Layer:
Validates and orders transactions (e.g., Ethereum's PoS).
Data Availability Layer:
Ensures transaction data is accessible (e.g., Celestia, Polygon Avail).
Settlement Layer:
Provides finality and dispute resolution (e.g., Ethereum).
Key Benefits
Scalability:
Offloads work to specialized layers, reducing congestion.
Flexibility:
Developers can customize components (like changing RAM in a PC).
Innovation:
Faster experimentation and development without rebuilding the whole chain.
Performance:
Optimized layers lead to faster transactions and lower fees.
Monolithic vs. Modular
Monolithic (e.g., early Ethereum, Bitcoin): One chain handles all functions, leading to bottlenecks.
Modular (e.g., Celestia, Cosmos, Polkadot): Functions are separated, allowing specialized scaling and better performance.
Analogy
Think of it like building a PC:
instead of one giant console (monolithic), you pick a motherboard, CPU, RAM, and GPU separately (modular) to build a machine perfectly suited for gaming, video editing, or general use.