What Is Sharding And Parallel Processing Techniques
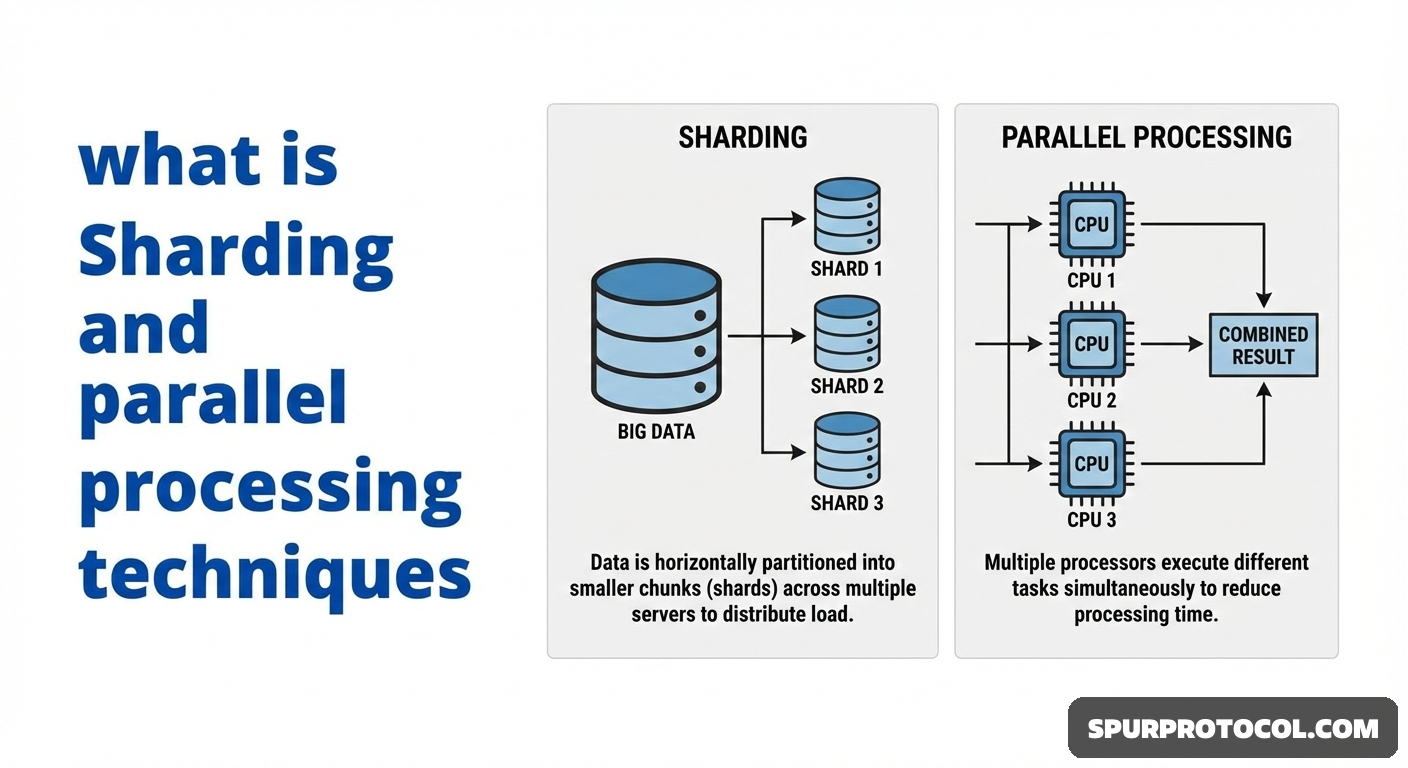
Sharding is a database partitioning technique that splits a large database into smaller, independent parts called shards, which are then stored across multiple machines. Parallel processing is a general computing technique that involves performing multiple operations or tasks simultaneously, and it is the mechanism by which sharding achieves its scalability benefits.
Go Back
🕒 6:23 AM
📅 Dec 14, 2025
✍️ By chyneyz
Sharding Explained
Sharding primarily addresses the challenges of scalability, performance, and storage capacity in systems with large data volumes and high traffic.
Mechanism: Sharding is a form of horizontal partitioning, where rows of data are separated into distinct physical databases. Each shard functions as a fully independent database with its own memory and disk, responsible only for a subset of the total data.
Purpose: The main goal is to distribute the workload, allowing the system to handle more data and more requests than a single machine could manage alone.
Key Concept:
Shared-Nothing Architecture: Sharded systems typically use a shared-nothing architecture, meaning the individual shards do not share computing resources (like memory or storage), which allows them to operate autonomously and in parallel.
Parallel Processing Explained
Parallel processing is a broader concept in computer science that enables systems to execute different parts of a task or multiple tasks at the same time.
Mechanism: Instead of processing tasks sequentially (one after the other), parallel processing breaks a complex task into smaller parts that can be executed concurrently by multiple processors or nodes.
Purpose: It is used to significantly boost speed, efficiency, and overall throughput, particularly for computationally intensive tasks or systems with heavy transaction volumes.
Relationship Between Sharding and Parallel Processing
Sharding is a specific implementation strategy that leverages the principles of parallel processing.
How they work together: By dividing the database into shards, a system can direct different queries or transactions to different shards simultaneously. Each shard processes its assigned data in parallel with other shards, meaning many operations are happening concurrently across the network, rather than sequentially on a single, massive database.
Result: This synergy is what allows large-scale applications (such as social media platforms, e-commerce sites, and blockchain networks like Ethereum and Zilliqa) to achieve high transaction speeds and performance, even as data volume and user load increase.
Common Sharding Techniques
Different methods are used to determine how data is distributed among shards.
Range-Based Sharding: Data is partitioned based on a range of values (e.g., customer IDs 1-1000 in Shard A, 1001-2000 in Shard B).
Hash-Based Sharding: A hash function is applied to a "shard key" (a specific data field) to pseudo-randomly determine which shard the data belongs to, ensuring an even distribution of data and preventing "hotspots".
Directory-Based Sharding: A central lookup table or service maintains a map of data to its corresponding shard, which offers flexibility in data distribution rules.
Geo-Based Sharding: Data is stored in shards based on geographic location to reduce latency for regionally dispersed users and comply with data locality regulations.
