What Is The Merkle Tree Used For In A Blockchain?
A Merkle Tree is a foundational data structure that uses cryptographic hashing to organize massive amounts of data into a single, verifiable hash (the Merkle Root). This tree structure is used in every block to summarize all transactions, providing efficient, trustless verification of data integrity and transaction inclusion.
Go Back
🕒 7:52 PM
📅 Oct 29, 2025
✍️ By Nathanael707
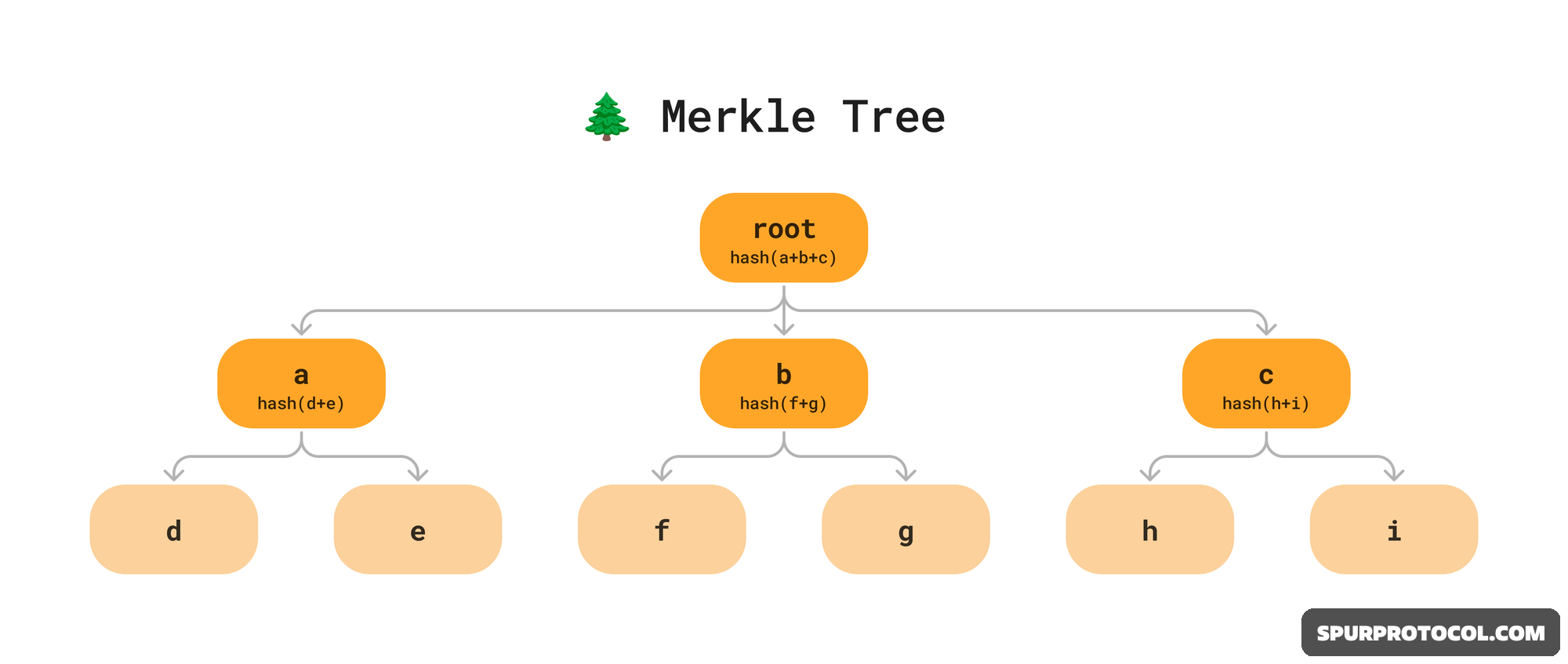
Defining the Merkle Tree StructureA Merkle Tree (or hash tree) is built from the bottom up. It involves pairing the hashes of individual data elements (transactions) and repeatedly hashing the resulting pairs until a single hash is generated at the very top.
Structure: A hierarchical tree of cryptographic hashes.
Leaves: The hashes of the individual transactions (at the bottom).
Branches: Intermediate hashes resulting from combining two child hashes.
Merkle Root: The final, single hash at the top, which is included in the block header.
Utility for Transaction Verification
The Merkle Tree is essential for light clients to securely verify transactions without downloading the full blockchain.
Inclusion Proof (Merkle Proof): A light client needs only the transaction hash, the Merkle Root, and the sister hashes along the path to the root.
Efficiency: Allows for the highly efficient verification of any data element within a massive set.
Data Tampering: Any change to a single transaction instantly invalidates the path and fails the check against the Merkle Root.
